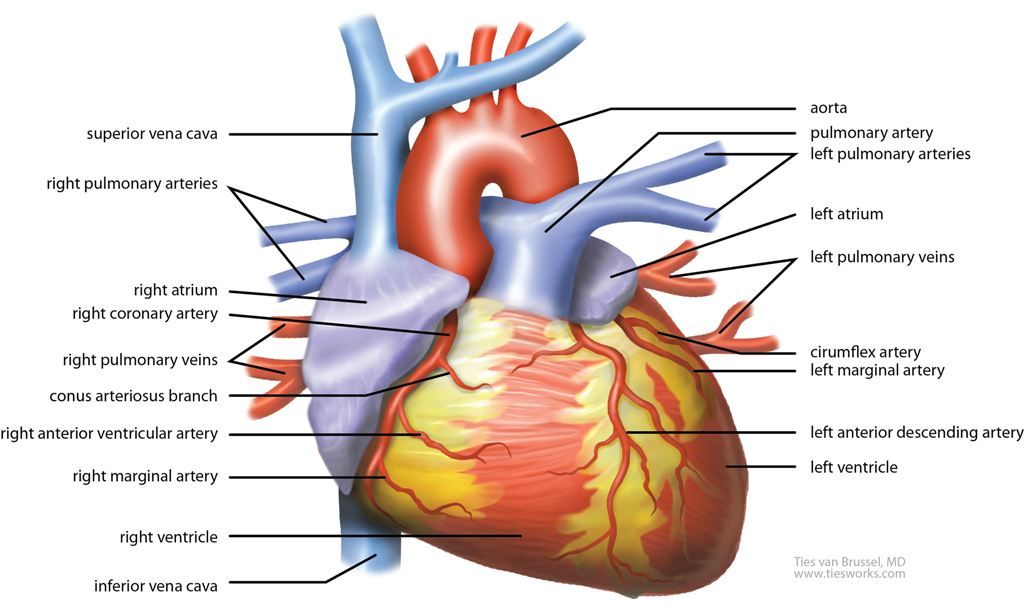
The Heart
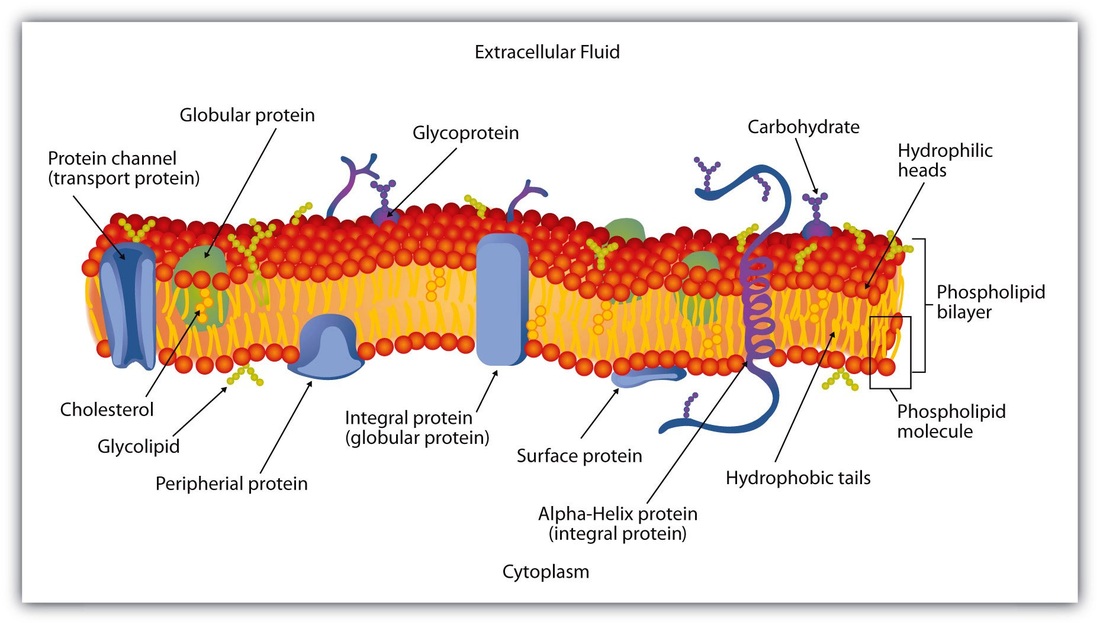
Cell Membranes

Click the Dropbox on the right to download the presentation on cell membranes:
Links to animations and interactive learning resources
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.

Click the Dropbox icon to download the questions on cell membranes:
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
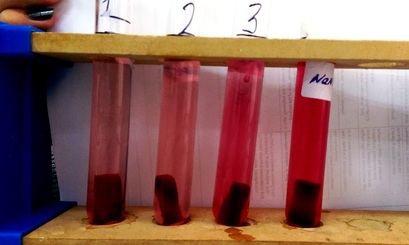
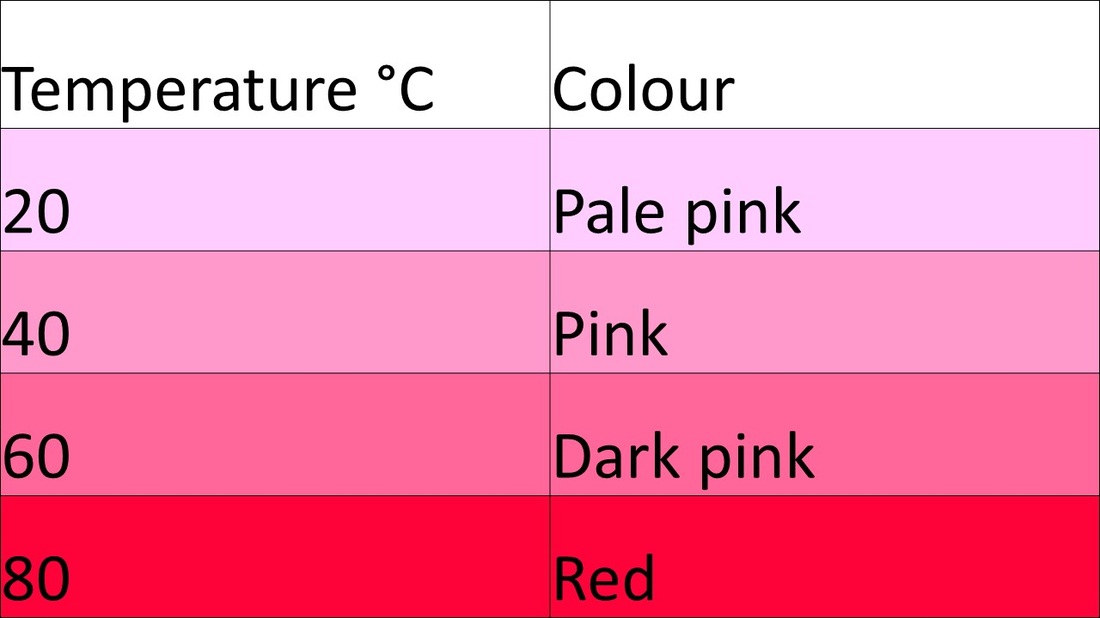
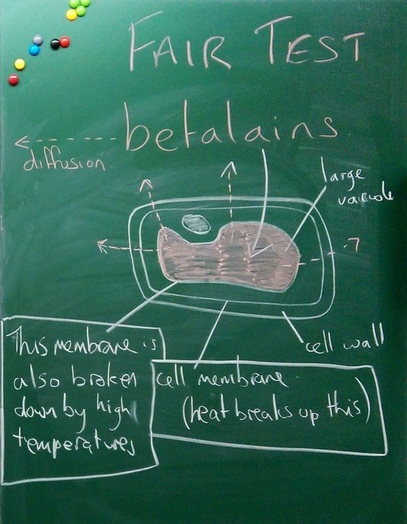
Results
Conclusions:
Cell Organelles

Link to resource covering the ultrastucture of plant cells including electronmicrographs.

Histology Learning System - The Ultrastructure of cells (Electron micrographs).
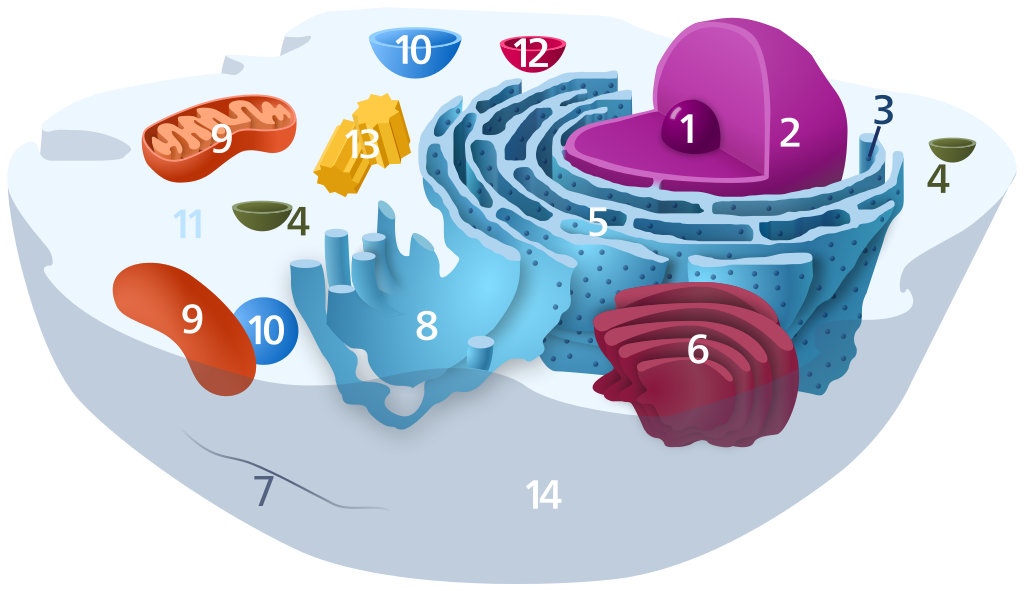
Components of a typical animal cell with Wikipedia hyperlinks:
- Nucleolus
- Nucleus
- Ribosome (little dots)
- Vesicle
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus (or "Golgi body")
- Cytoskeleton
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondrion
- Vacuole
- Cytosol (fluid that contains organelles)
- Lysosome
- Centrosome (Centrioles)
- Cell membrane
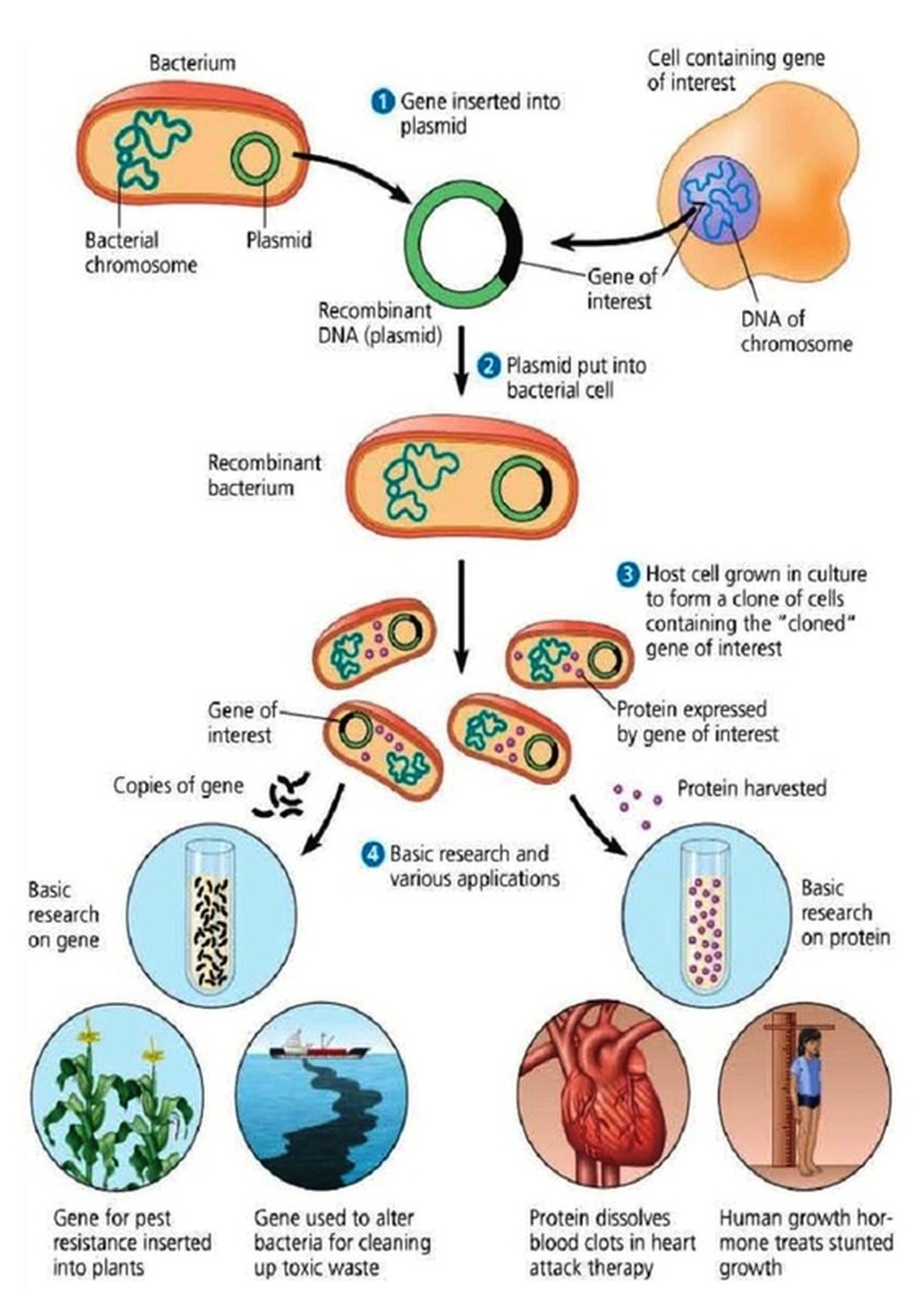
Classification of Bacteria
Bioreactors
Click the icon to attempt the crossword
Stages in the thermocycler
Heat to 90-95°C - DENATURES/separates the DNA strands through breaking the weak hydrogen bonds
Cool to 50-55°C - ANNEALS (joins) the primers to the DNA strands
Heat to 75°C - Optimum temperature for the Taq polymerase to ELONATE the DNA strands
The cycle is repeated resulting in an exponential increase in the amount of DNA (AMPLIFICATION)
Heat to 90-95°C - DENATURES/separates the DNA strands through breaking the weak hydrogen bonds
Cool to 50-55°C - ANNEALS (joins) the primers to the DNA strands
Heat to 75°C - Optimum temperature for the Taq polymerase to ELONATE the DNA strands
The cycle is repeated resulting in an exponential increase in the amount of DNA (AMPLIFICATION)